While climate change spells trouble for much of the southern hemisphere, it’s quietly putting Greenland on the global map, not just as a symbol of the climate crisis, but as a rising player in 21st-century geopolitics. As Arctic ice gives way to open water and new shipping lanes, the world’s major powers are turning their gaze northward. This Arctic Island is a self-governing territory within the Kingdom of Denmark with its own parliament and control over most domestic matters, now finds itself at the center of a strategic scramble.
Greenland and it’s Strategic Importance
Rich in rare earth minerals, graphite, and other critical resources, Greenland is becoming a prize in the international race to secure materials essential for renewable energy, technology, and defense industries. As Arctic shipping routes open, the island’s value grows not only for its wealth beneath the ice but also for its location along emerging trade corridors that could reshape global commerce.
The United States has ramped up its engagement by reopening its consulate in Nuuk and investing in infrastructure and resource mapping, signaling an intent to counterbalance rivals and lock in its access to the island’s mineral wealth and strategic routes. Washington views Greenland not only as a resource hub but as a critical outpost for monitoring Russian and Chinese activity in the Arctic.
The Arctic Powers fighting for Greenland
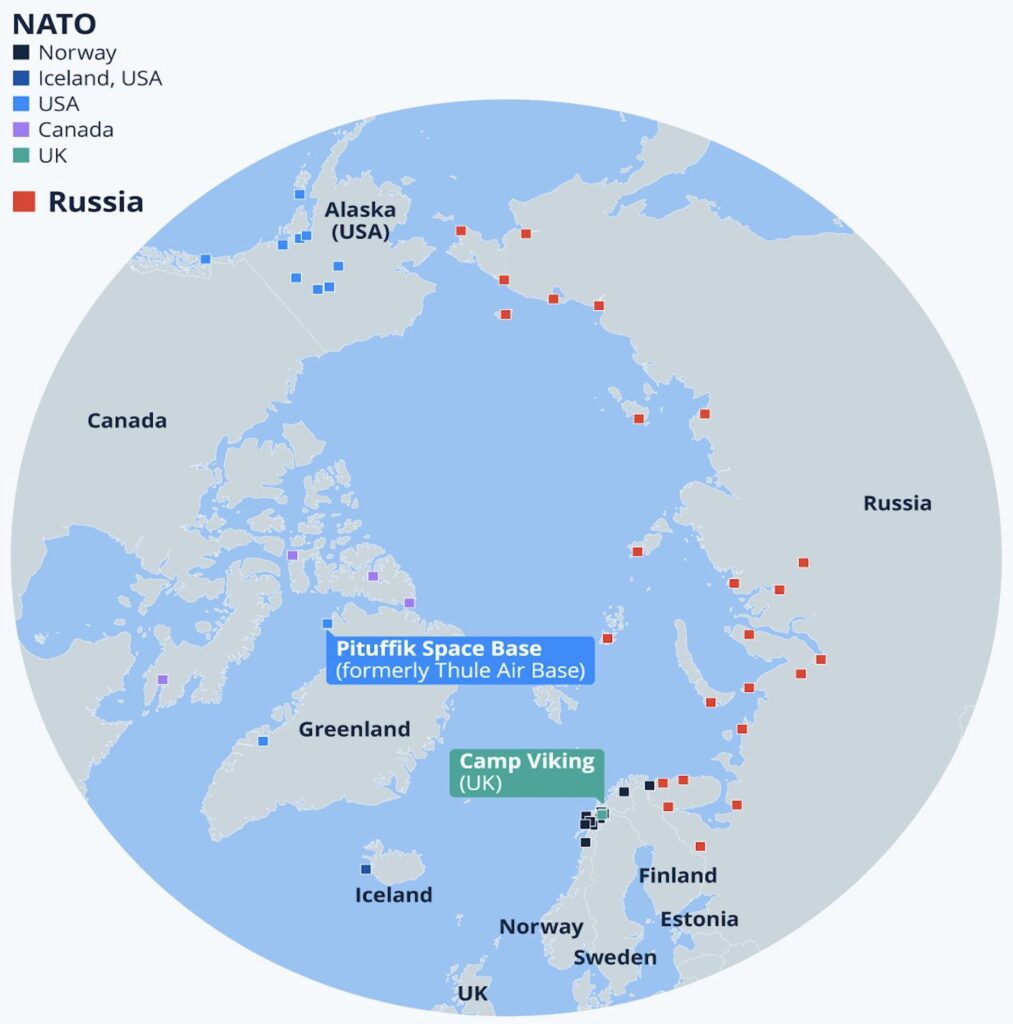
- United States: Determined to stay ahead of global competitors, the U.S. is deepening diplomatic and economic engagement with this artic island. American officials see the island as a future hub for critical raw materials and military monitoring.The shortest route for Russia to ever launch missiles or attack the US would be through the Arctic and Greenland area, thus the newfound interest that US has towards ensuring its presence in the arctic.
- Russia: Moscow, investing in ports, bases, and a nuclear icebreaker fleet, sees the Arctic, this remote arctic territory included as vital to its economic and security future. Trade routes across the top of Russia, now opening due to rising temperatures, could soon rival traditional ones through the Suez Canal, promising faster travel for global shipping.
- China: Calling itself a “near-Arctic” state, China has tried to secure a foothold in Greenland through mine investments, infrastructure projects, and research stations, though Denmark and the U.S. have blocked several high-profile ventures. Despite setbacks, China is persistent, seeking long-term access to rare earths and a role in “Polar Silk Road” trade.
- European Union: The EU is pursuing closer partnership with the arctic territory, aiming to lock in reliable supply chains for green technology minerals while keeping influence in Western hands. The EU works with Denmark on sustainable development and independence support, investing in research and infrastructure to counterbalance Chinese and Russian moves.
Greenland’s Path Forward

Caught between competing superpowers, Greenland treads carefully. While the government welcomes selective foreign investment, it does so strictly on its own terms. For instance, its 2021 ban on uranium mining highlighted Greenlanders’ strong commitment to protecting the environment and maintaining local autonomy, even at the cost of short-term economic gain.
However, public opinion remains divided. On one hand, some native Greenlanders view mining as a potential path to full independence from Denmark. On the other hand, many worry about the environmental risks and the possible harm to Indigenous ways of life. In response, the country’s leaders emphasize that any major decisions must reflect the will of the people, not the interests of foreign powers.
An Uncertain Future for Greenland?
Climate change is reshaping the world map, moving Greenland from the periphery to center stage. Melting glaciers, once a warning of planetary peril, now draw investment, ambition, and anxiety. The question remains: Will Greenland become another great-power battleground, or can it set its own course grounded in autonomy and sustainability? For now, its future rests in the hands of its people, striving to balance global interest with preservation of their fragile Arctic home.
For more such informative articles, Checkout theWorldTimes.



