As international adoption rates continue their alarming decline, fewer children are being adopted into permanent homes across the globe. Why is “Fewer Arms Open” changing, and what does this mean for children who are at risk, and waiting for families?
Drop in Adoption

Worldwide, and especially in the US, the number of international adoptions has been dropping. Although the number of adoptions in the US peaked in 2004 at over 22,000, it has since fallen to less than 2,000.
UNICEF acknowledges the significant drop in international adoptions in recent years. UNICEF’s primary goal is to keep families together whenever possible, and to explore alternatives to institutional care for children who cannot remain with their families.
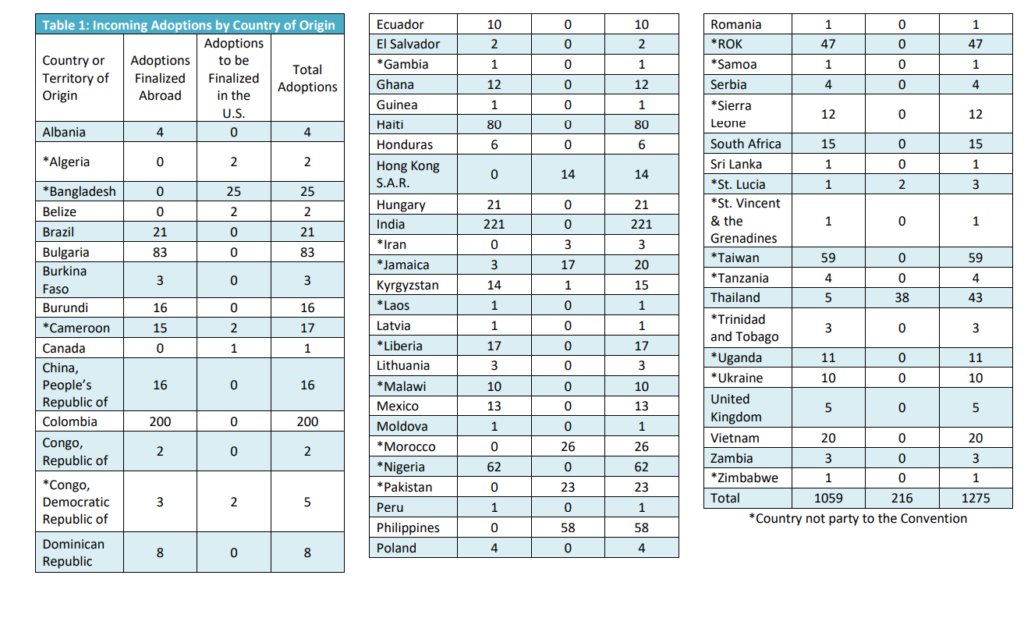
The number of international adoptions has significantly decreased in the primary receiving countries, such as the United States. China, Colombia, and India were once the main countries from which adoptees came. But now their numbers have also declined.
This trend raises concerns despite the complex factors driving the change.
Why Are Adoptions Falling?
Increased Regulations, and Ethical Concerns on Adoption.
A number of factors, such as tighter regulations, fewer adoptable children, and worries about child trafficking, and unethical behavior, are contributing to the decline in international adoption rates. Stricter regulations, higher prices, and less availability are the results of these factors, which have also contributed to the general drop in international adoptions.
- The Hague Convention on International Adoption was established to regulate international adoptions, and prevent child trafficking, exploitation, and abduction. It prioritizes the child’s best interests by giving domestic adoption precedence over options from other countries.
- The subsidiarity principle of the convention, which promotes placing children in their country of origin. This has reduced the number of children available for international adoption, particularly in countries with increasing domestic adoption rates.
- The decline in adoptions from Russia, and China is often used to illustrate the convention’s impact. China recently banned international adoptions (except for blood relatives), and decided to prioritize domestic adoptions, in part because of the convention.
Decreased Availability of Adoptable Children.
- Lower infant mortality rates, and fewer orphaned, or abandoned children are the results of better healthcare, economic growth, and expanded educational opportunities in many countries of origin.
- In an effort to keep children in their own communities, and cultures, some nations are giving domestic adoptions priority.
- Special needs (medical, developmental, or emotional) now make up a greater percentage of children up for international adoption, which could be a turnoff for some potential adopters.
Political, and Economic Factors affecting Adoption:
- Concerns about national identity, cultural preservation, or the effects of mass adoptions on their populations have led some nations to enact laws that limit, or outright prohibit international adoptions.
- International adoption programs may be suspended, or terminated as a result of political tensions, and sanctions between nations, which can also affect adoption agreements.
- Many families may find the higher expenses of international adoption to be a deterrent.
With adoption rates continuing to decline, and fewer arms open to children in need, the challenges are clear. The question remains: how can the global community ensure that every child has the opportunity to thrive in a loving, and permanent home?
For more such informative articles, stay tuned at The World Times.



